 |
Only
a very tiny percentage of diamond rough production is suitable
for cutting and use in jewellery.
In judging the quality–and therefore the value–of
a cut diamond, buyers must take into account four criteria, known
as the:
Four C's
Colour – Clarity – Carat
weight – Cut
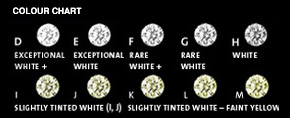
Colour
Colourless stones are extremely
valuable, while yellow or brown-tinged stones are
regarded as imperfect and therefore less valuable.
Many people are also unaware that diamonds can come in every colour under the
rainbow and in many different
intensities of colour. These are highly
prized by collectors and jewellery designers the world over for their phenomenal
rarity and beauty.
Coloured diamonds are available on request.
|
Fluoresence
in Diamonds
Some people like
the effect fluorescence or “photoluminescence” produces
in diamonds while others do not. Under
normal conditions it is never seen unless
the diamond
displays a very high fluorescence. In this
case, when a stone that displays unusually
high fluorescence
is exposed to direct or intense ultraviolet
light a bluish glow can be observed. Fluorescence
is
caused by trace elements of boron found
in the diamond which when activated by
UV light, give
you a sometimes blue white colour.
These “blue white stones” were
highly sought after in the past as they
can seem much brighter than their non fluorescent
counterparts. Extreme
fluorescence in a diamond can lower the price, but in some cases it can
even lift the colour one grade to the naked
eye and
in recent years GIA have stated that typically fluorescence can be a plus
in certain diamonds.
We however rarely buy or sell strong fluorescent diamonds unless we feel them
to be of exceptional beauty. Listed below are the abbreviations for describing
strength of fluorescence:
• N, NO, NON - No Fluorescence
• F, FB, FT, FA - Faint or Faint Blue Fluorescence
• S, ST, STB, STG - Strong Fluorescence
|
 |